TECHNOLOGY
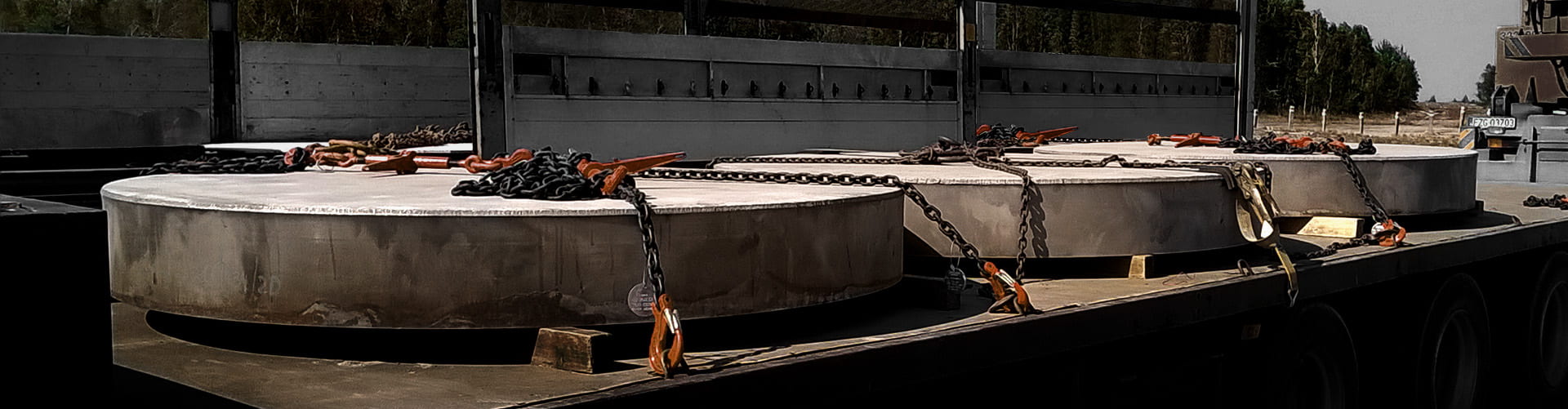
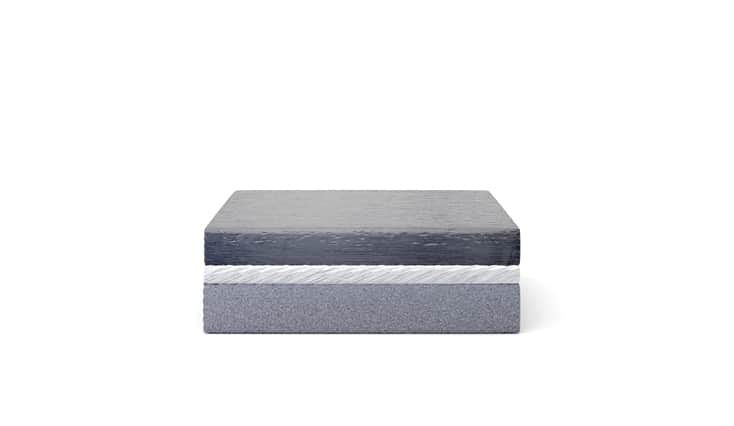
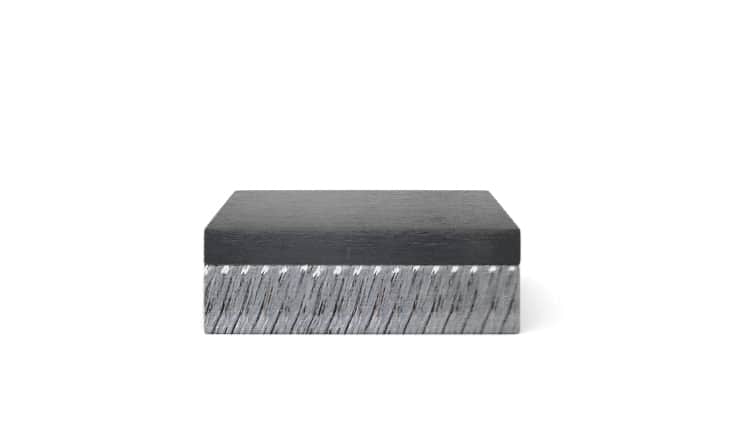
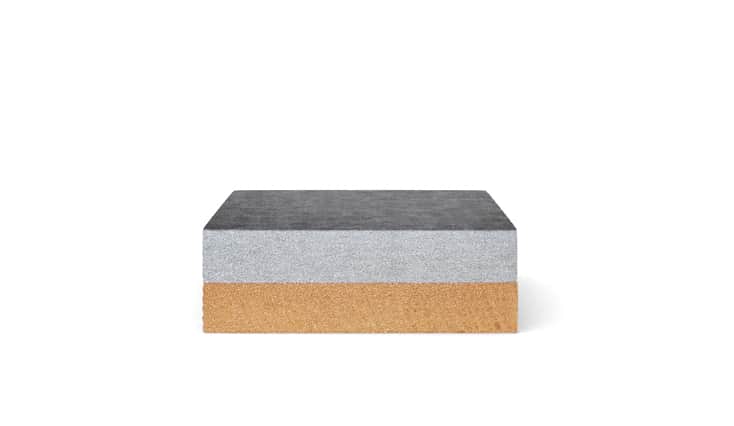
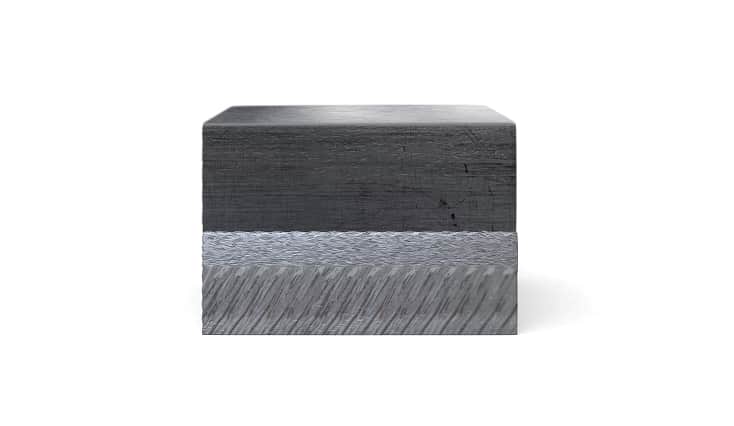
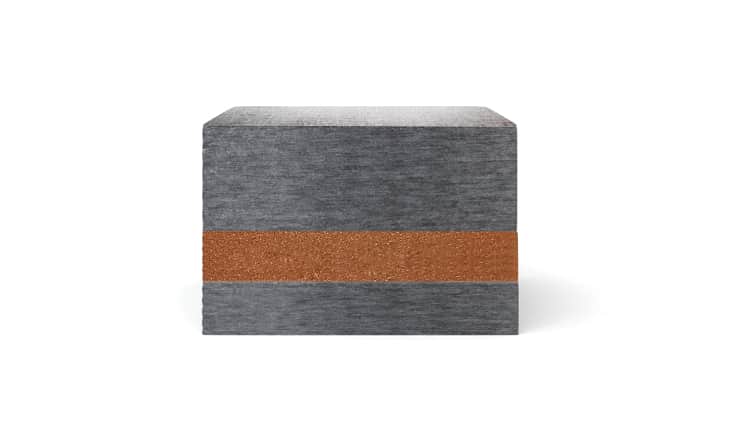
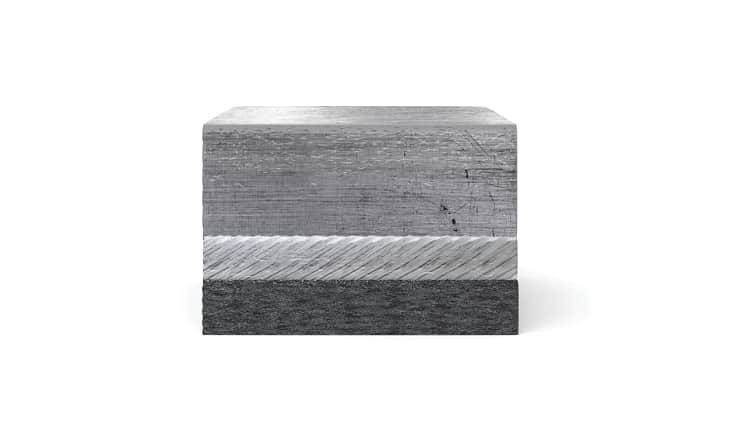
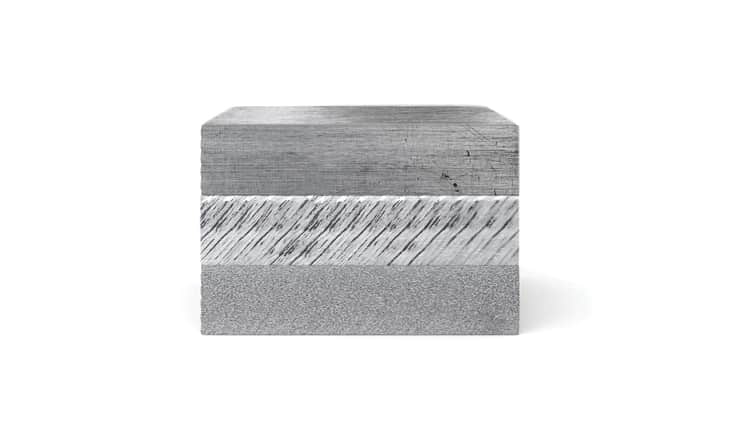
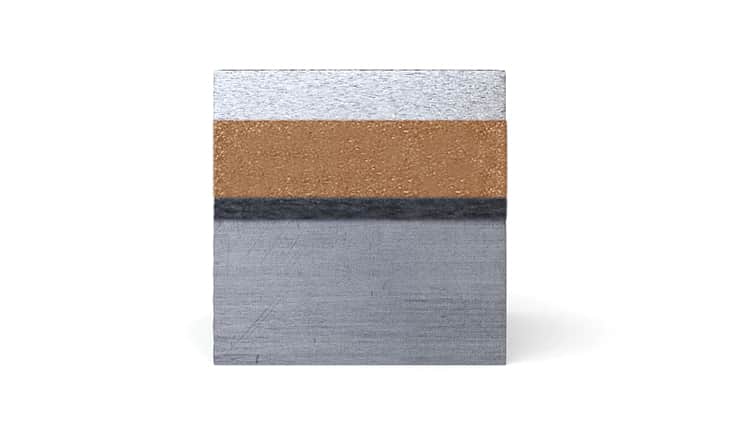
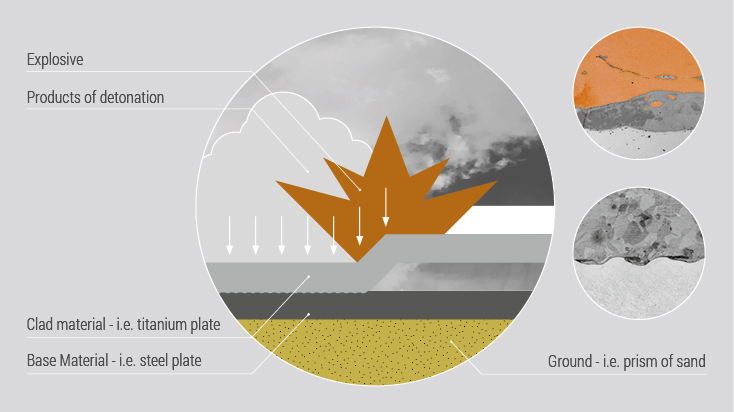
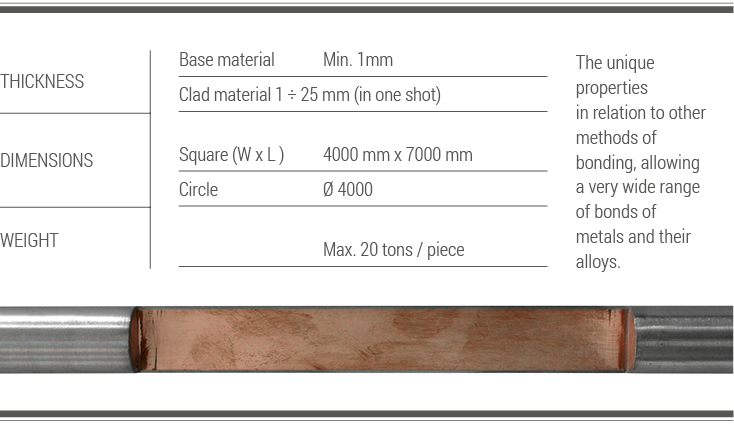
An explosion is commonly associated with destructive action. Explosive cladding technology uses the phenomenon of explosion in a creative way and is of great technological importance in the production of advanced metal composites. It complements conventional methods of producing clad elements, such as overlay welding and roll-bonding. This technology allows joining metals and their alloys, impossible to connect by other industrial methods.